History of Augmented Reality and the difference with VR
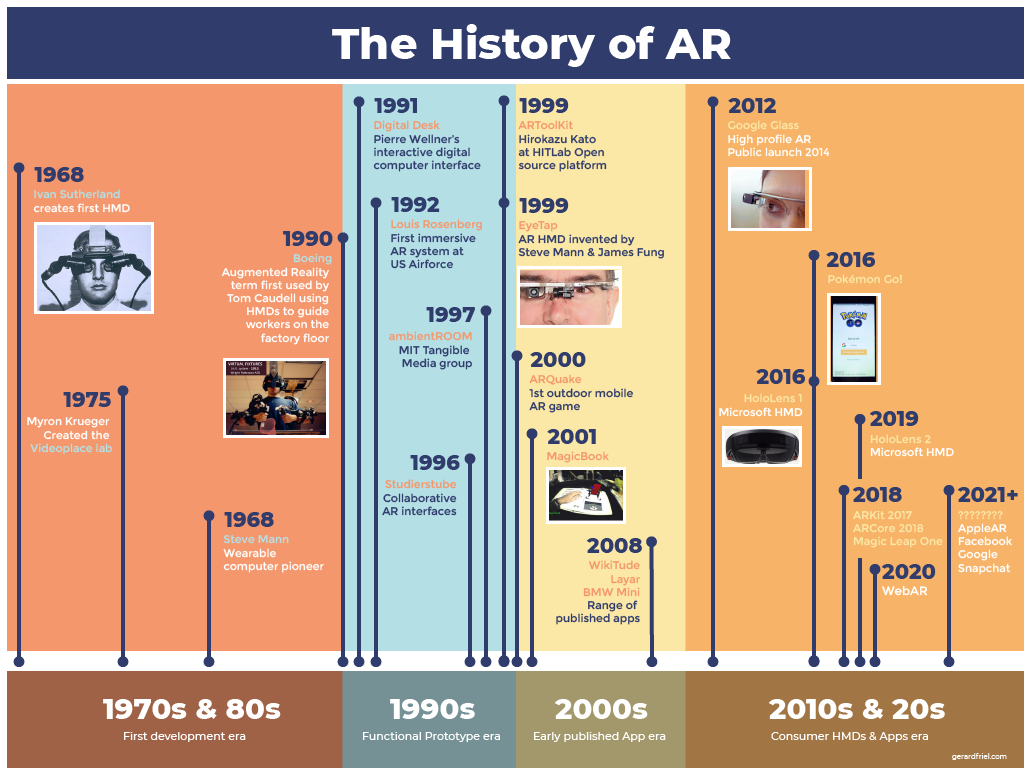
To get a better understandig of AR we have gone back to the very first beginning. We discovered that the history of augmented reality (AR) a relatively recent but rapidly evolving field is that combines elements of computer technology, digital information, and the real world. AR overlays digital information and virtual objects onto the physical world, enhancing a user's perception of reality. Here's an overview of the key milestones in the history of AR:
1. Early Concepts (1960s-1980s): - Ivan Sutherland, a computer scientist, is often credited with laying the foundation for AR with his work on the "Sword of Damocles" in the 1960s. This was a head-mounted display system that allowed users to see simple computer-generated graphics superimposed on their view of the real world. - In the 1970s and 1980s, researchers continued to explore the possibilities of AR, but the technology was still in its infancy.
2. AR Displays (1990s-2000s): - The 1990s saw the development of wearable AR displays, such as the Virtual Fixtures system by Louis Rosenberg, which aimed to enhance military training and industrial applications. - The term "augmented reality" was coined by Boeing researcher Tom Caudell in 1990 to describe a digital display system used by assembly line workers. - In the late 1990s and early 2000s, AR research gained traction, and several companies began exploring commercial applications.
3. Smartphone Era (2010s-Present): - The proliferation of smartphones with built-in cameras, GPS, and powerful processors in the late 2000s and early 2010s opened up new possibilities for AR. - In 2013, Google introduced Google Glass, a wearable AR device that displayed information in a heads-up display. - In 2016, Pokémon GO, an AR mobile game, became a global phenomenon, demonstrating the potential of AR for entertainment. - Tech giants like Apple and Google invested heavily in AR development, with Apple introducing ARKit in 2017 and Google launching ARCore in 2018 to enable AR experiences on mobile devices. - The use of AR expanded beyond entertainment into various fields, including healthcare, education, retail, and marketing.
4. Mixed Reality (MR) and Smart Glasses: - In the 2010s, companies like Microsoft developed mixed reality headsets like the HoloLens, which combine AR and virtual reality (VR) to create immersive experiences. - Several companies, including Microsoft, Magic Leap, and others, have been working on smart glasses that aim to seamlessly integrate digital information into the user's field of view.
5. Future Prospects: - AR continues to advance, with developments in computer vision, machine learning, and hardware. - Industries like healthcare, architecture, automotive, and education are exploring innovative AR applications. - AR is also making inroads in remote collaboration, allowing users to share their augmented reality experiences with others. The history of AR is marked by a steady progression from early experimental concepts to widespread commercial applications. As technology continues to evolve, AR is likely to become an integral part of our daily lives, transforming how we interact with the world around us.
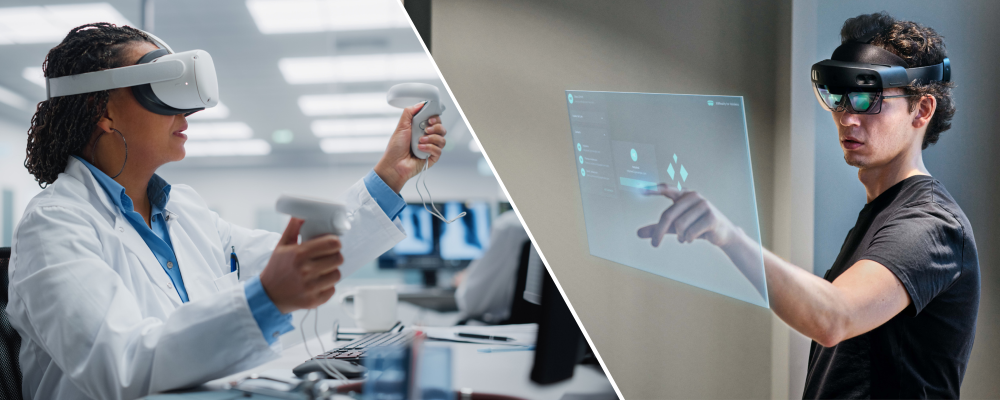
Below there are some additions and emphases to give a good description of the difference between Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): 1. **Full Immersion vs. Added Information:** - In VR, you are completely immersed in a virtual world. Everything you see and experience originates from that virtual environment. You cannot be aware of the real world around you. - In AR, you remain connected to the real world, and digital information is added to your field of view. The goal is to integrate useful information, graphical overlays, or virtual objects into the real world. 2. Equipment: - VR headsets, such as the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive, are often connected to powerful computers and typically offer a more intense and visually immersive VR experience. However, there are also standalone VR headsets, like the Oculus Quest, which have a built-in computer. - AR devices range from headsets like the Microsoft HoloLens to AR glasses like Google Glass. AR can also be experienced through smartphones or tablets using the device's cameras and screen. 3. Interaction: - In VR, users can often interact with the virtual environment using hand controllers or hand gestures within the virtual world. - In AR, interactions can occur through hand gestures, voice commands, or touch screens, depending on the device. Interactions often focus on manipulating the digital elements added to the real world. 4. Applications: - VR is frequently used for gaming, simulation training, virtual travel, and entertainment. - AR has applications in navigation, education, industrial maintenance, medical procedures, as well as everyday consumer applications like shopping, advertising, and social media (such as filters on Snapchat). In summary, VR offers a fully immersive experience in a virtual world, while AR enhances the real world with digital information and objects.
Pictures from: https://www.gerardfriel.com/wp-content/uploads/Augmented-reality-timeline.png


Reacties
Een reactie posten